Understanding What Aesthetic Medicine Is
Aesthetic medicine is a medical discipline focused on improving a person’s appearance through non-invasive to minimally invasive procedures. Unlike plastic surgery, which often involves major surgical interventions, aesthetic medicine emphasizes treatments with less downtime and risk. The goal of aesthetic medicine is not just to correct physical flaws but to enhance a person’s natural beauty, boost their confidence, and improve their overall well-being.
The Rise in Popularity of Aesthetic Medicine
The field of aesthetic medicine has seen explosive growth over the past few decades. This rise can be attributed to several factors:
- Technological advancements: Innovations in lasers, injectables, and energy-based devices have made aesthetic medicine procedures more effective and safer.
- Changing social perceptions: The stigma once associated with cosmetic procedures has largely diminished, making aesthetic medicine more socially acceptable.
- Increased accessibility: The wide availability of clinics and the lower cost of many aesthetic medicine treatments compared to surgery have made them accessible to a broader demographic.
- Influence of social media: Platforms like Instagram and TikTok have popularized aesthetic medicine by showcasing its results and making discussions around it more common.
Key Treatments and Procedures in Aesthetic Medicine
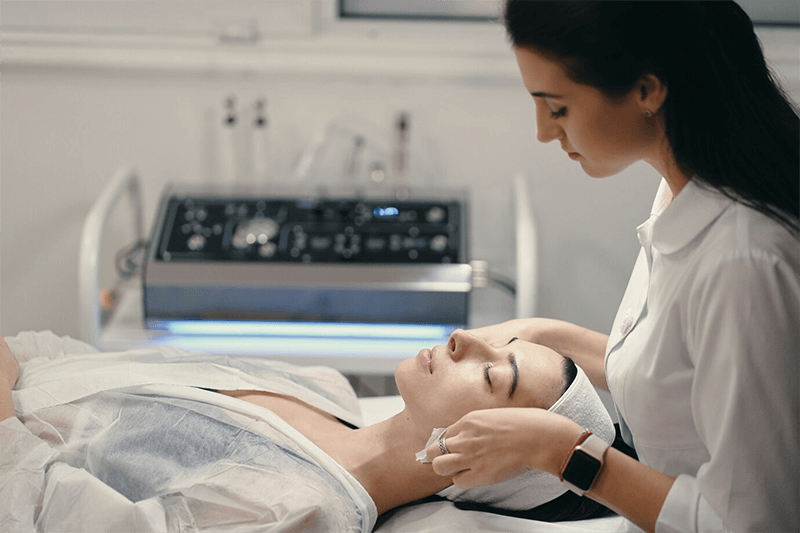
Injectable Treatments
Injectables are a cornerstone of modern aesthetic medicine, offering powerful results with minimal invasiveness.
- Botulinum Toxin (Botox): A staple in aesthetic medicine, Botox is used to temporarily relax facial muscles and reduce the appearance of dynamic wrinkles, such as crow’s feet and frown lines.
- Dermal Fillers: These are used in aesthetic medicine to restore volume, smooth out deep wrinkles, and enhance facial features like the lips and cheeks. Fillers are a versatile tool in aesthetic medicine.
- PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) Therapy: A regenerative treatment in aesthetic medicine, PRP uses a patient’s own blood to stimulate collagen production and improve skin texture.
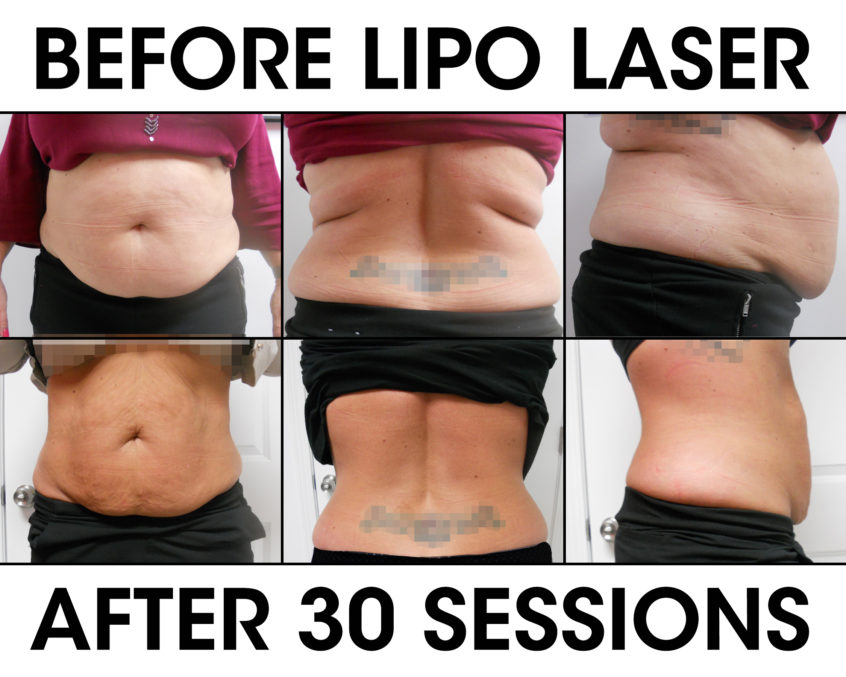
Energy-Based Devices
Technology plays a crucial role in modern aesthetic medicine, and energy-based devices are a prime example.
- Laser Treatments: Aesthetic medicine uses lasers for a variety of purposes, including skin resurfacing, hair removal, and tattoo removal.
- Radiofrequency (RF) and Ultrasound Treatments: These devices are employed in aesthetic medicine for skin tightening and body contouring by stimulating collagen and elastin production.
Skincare and Chemical Peels
These treatments are essential components of a holistic approach to aesthetic medicine.
- Chemical Peels: Aesthetic medicine professionals use chemical peels to exfoliate the top layers of skin, addressing concerns like acne, uneven pigmentation, and fine lines.
- Medical-Grade Skincare: Beyond a single treatment, the foundation of aesthetic medicine includes a tailored skincare regimen with products that are more potent than over-the-counter options.
The Role of a Professional in Aesthetic Medicine
The Importance of a Qualified Practitioner
When considering aesthetic medicine, the choice of practitioner is paramount. A qualified doctor or nurse specializing in aesthetic medicine ensures safety and effective outcomes. They have a deep understanding of facial anatomy and the nuances of various aesthetic medicine procedures.
Personalizing Treatment Plans
A hallmark of high-quality aesthetic medicine is a personalized approach. A skilled practitioner in aesthetic medicine will:
- Conduct a thorough consultation: They will discuss the patient’s goals, medical history, and expectations.
- Develop a customized plan: Based on the consultation, they will create a tailored treatment plan using the most suitable aesthetic medicine techniques.
- Manage expectations: A professional in aesthetic medicine will provide a realistic outlook on the results and potential risks.
The Future of Aesthetic Medicine
Non-Invasive Technologies
The future of aesthetic medicine is leaning towards even more advanced, non-invasive treatments. We can expect innovations that offer more dramatic results with even less downtime. This is the direction where aesthetic medicine is headed.
The Intersection of Regenerative and Aesthetic Medicine
The line between regenerative medicine and aesthetic medicine is blurring. Treatments using a person’s own cells, like PRP and stem cell therapies, are becoming more common in aesthetic medicine. This trend focuses on stimulating the body’s natural healing and rejuvenation processes.
Ethical Considerations in Aesthetic Medicine
As the field of aesthetic medicine grows, so do the ethical questions. Discussions are ongoing about:
- Patient consent: Ensuring patients fully understand the risks and benefits of aesthetic medicine procedures.
- Regulation of practitioners: The need for standardized training and certification for all who practice aesthetic medicine.
- The influence of social media: Addressing the pressure to conform to unrealistic beauty standards promoted by social media and how it impacts the practice of aesthetic medicine.